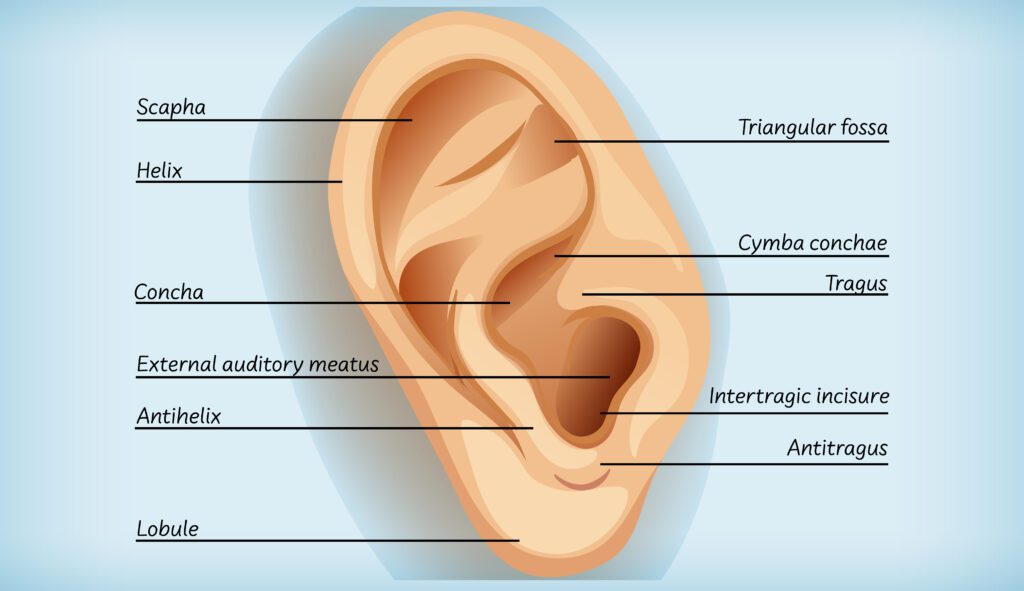
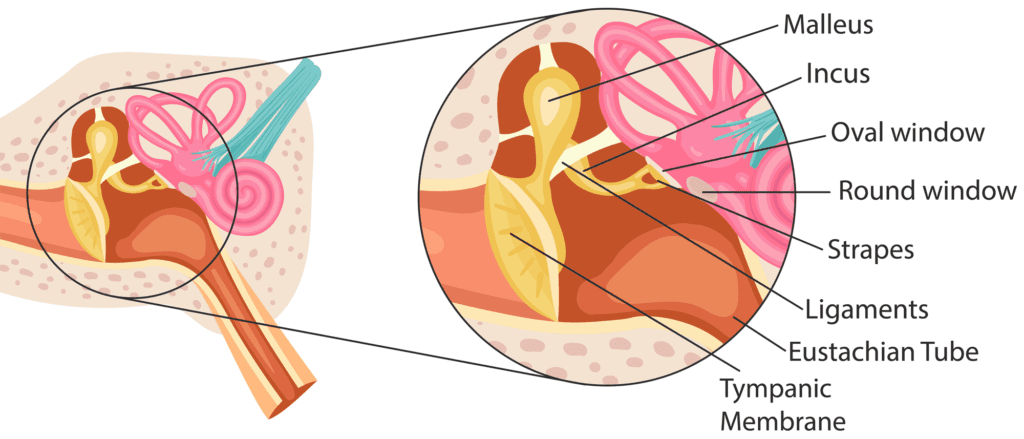
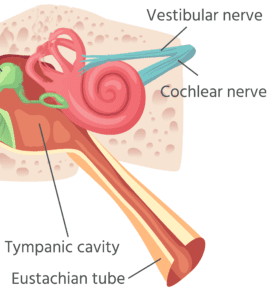
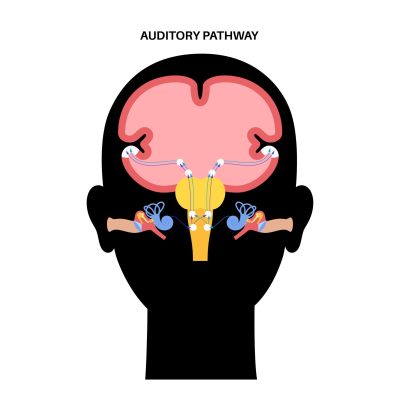
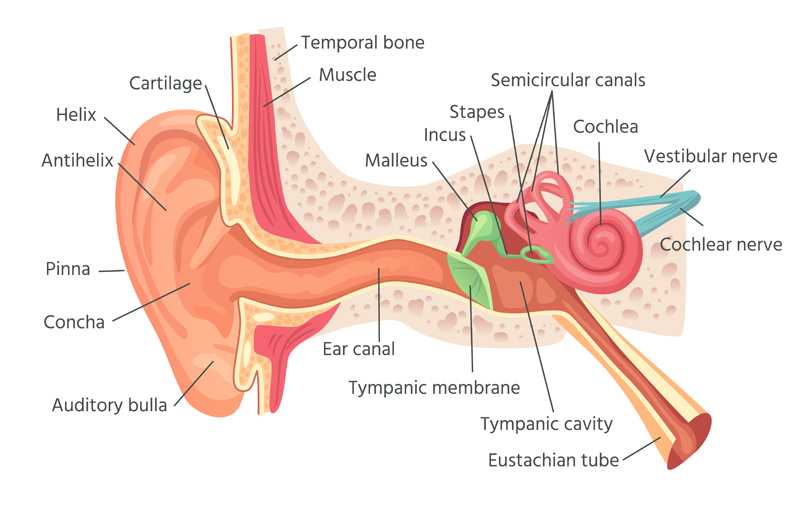
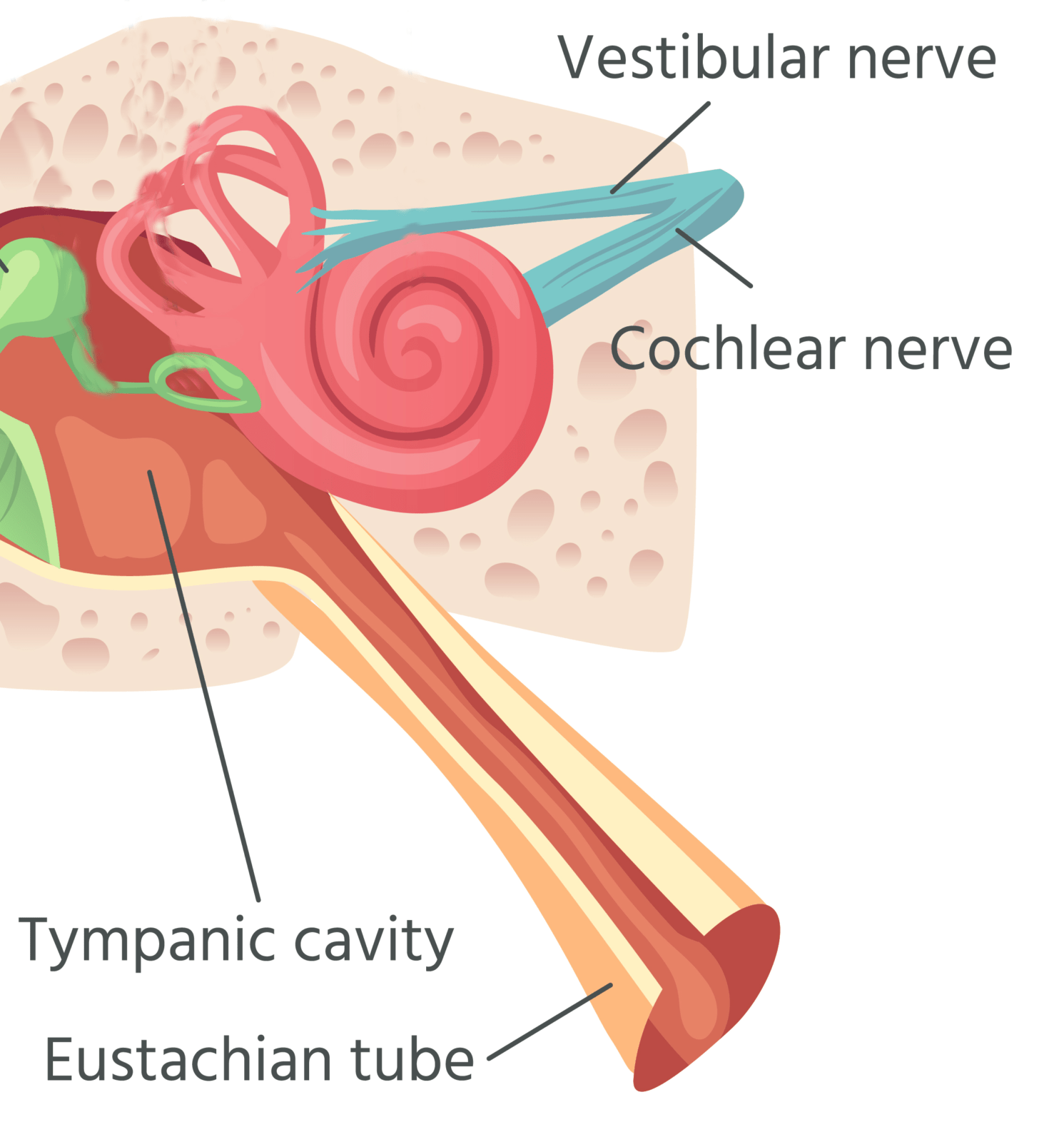
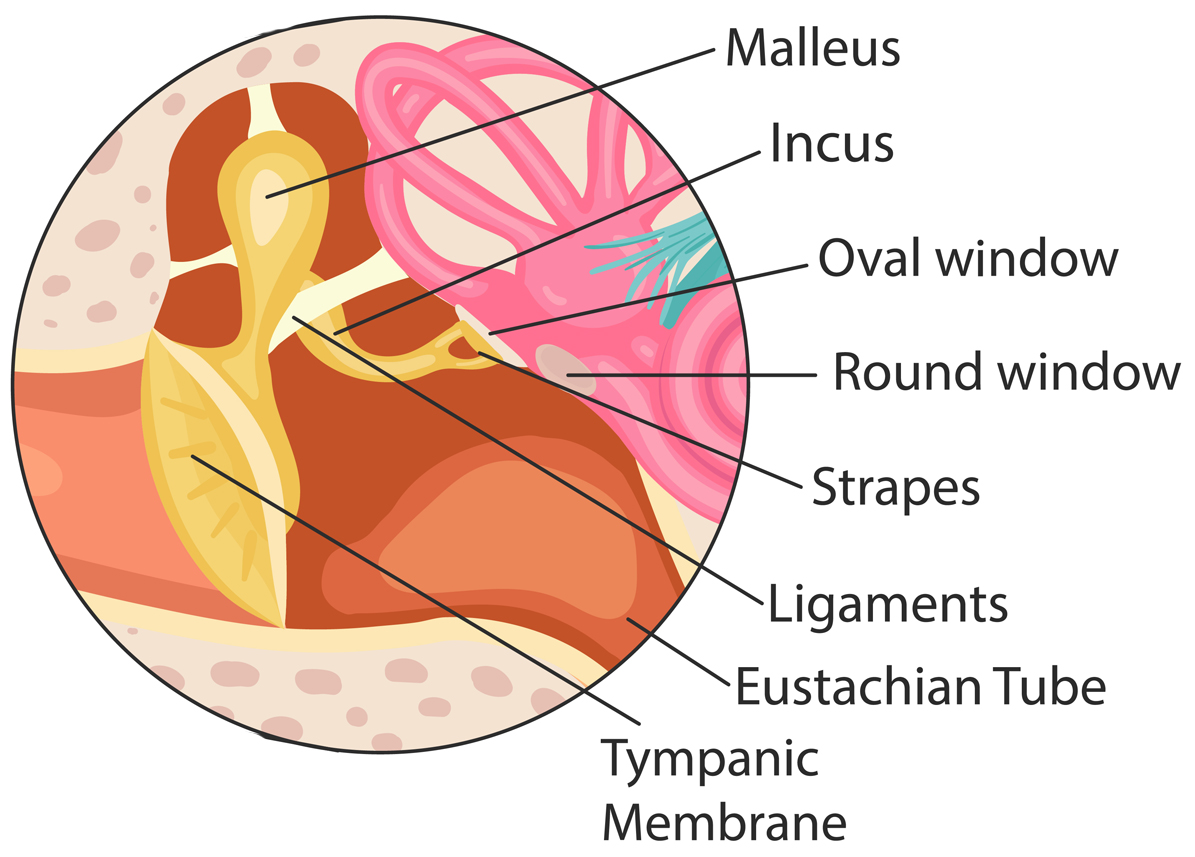
- Quiet
- Small Groups
- Public Transportation
- Group conversations
- Restaurants
- Meetings
- Outdoor activities
- Shopping/ Public Space
| Hearing Aid Technology | Quiet | Small Groups | Public Transportation | Group conversations | Restaurants | Meetings | Outdoor activities | Shopping/ Public Space |
| Hearing Aid Technology | $3999 /year | $3999 /year | $3999 /year | $3999 /year | $3999 /year | $3999 /year | $3999 /year | $3999 /year |
| Premium | ||||||||
| Mid | ||||||||
| Entry | Buy Now | Buy Now | Buy Now | Buy Now | Buy Now | Buy Now | Buy Now | Buy Now |